Hypertensive Crisis
END ORGAN DAMAGE:
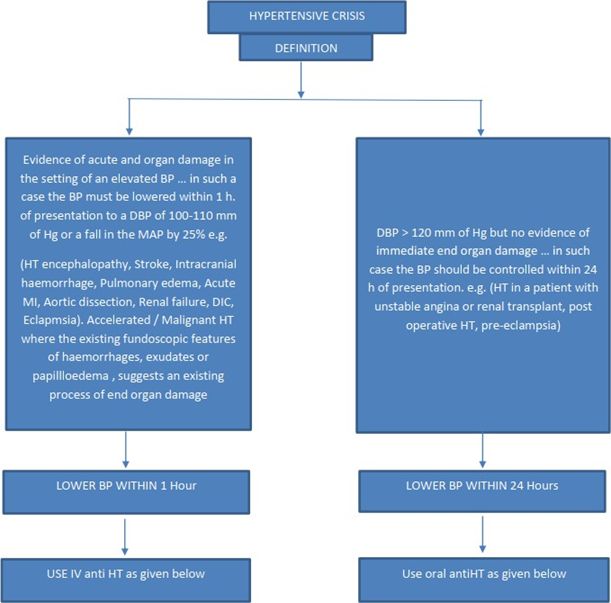
· HT encephalopathy: Presence of CNS dysfunction in a setting of SEVERE HT. Headache,depressed consciousness, vomiting, +/- seizures, +/- focal neurological deficits (if thesepersist, consider a cerebrovascular accident.)
· Retinopathy: cotton wool exudates, haemorrhages, papilloedema.Stroke/ Intracranial haemorrhage: focal deficits, raised ICT, vomiting, headache, loss of consciousness , +/- neck stiffness.
Do not treat HT in acute ischemic STROKE unless one of the following co-exists:
1. DBP=>130mm of Hg
2. Evidence of end organ damage
3. HT encephalopathy
· CCF/ unstable angina/MI
· Renal: worsening of proteinuria, hematuria, renal function.
· Hematological : Microangiopathic haemolytic anemia, DIC, Thrombocytopenia.
· HELLP syndrome (severe HT in pregnancy – ecclampsia): Hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes,low platelets.
INVESTIGATIONS:-
As in case of a hypertensive to look for end organ damage.TARGET ORGAN DAMAGE………Brain,Heart, Kidney, Vessels.
SCREEN FOR SECONDARY HT……. Electrolytes (K+), 24hr VMA and potassium in urine,
renal USGDoppler, tests for Cushings (overnight DST)
Look for associated risk factors-Lipids, Blood glucose. Consider the following in case of a pregnant lady:-
· Platelets (thrombocytopenia),
· Peripheral blood smear (schistocytes in microangiopathic hemolysis),
· LFT (elevated enzymes) MANAGEMENT OF HT CRISIS
In the presence of end organ damage, parenteral anti-hypertensives are recommended.
· For patients with acute ischemic coronary symptoms, NITROGLYCERINE is preferref tonitroprusside. (IV infusion)
· In pregnancy, alpha-methyl dopa, nifedipine and labetolol appear safe.
· Captopril is the drug of choice for Scleroderma renal crisis.
· In aortic dissection, combine nitroglycerine/nitroprusside with a betasdrenergic blocker eg.Propranolol to prevent further dissection.
Drugs | Dosages | Onset | Peak | Side-effects |
Nitroglycerine | 5mcg /min, can go upto 400 mcg/min at increments of 5- 10 mcg till desired effect. | 1-2 mins | 3-5 mins | Headache, vomiting Tachyphylaxis |
Sodium nitroprusside | 50- 100mcg/min, (0.3-10 mcg/kg/min) | Immediate | 2-3 min | Vomiting, Thiocyanate toxicity |
Do not start these drugs in the casualty without close monitoring before transferring the patient tothe ICU/WARD.
Monitor during patient transport also.
Add on cerebral antioedema measures to bring down the ICT.
Management:- in the absence of acute end organ damage, the anti HT therapy should be throughoral route.
Drugs | Dose | Onset | Peak | Duration | Side effects |
Aldomet | 250mg, repeat 6-8h | 2-4h | 4-6h |
| Headache, Vomiting |
Minoxidil | 1.25-20 mg PO 12 hourly | 1 hour | >1hr | 24h | Tachycardia angina |
Furosemide (Lasix) can be added on to any of these for enhancement of action. (Dose 40-80 mg PO,repeat 6th hourly).
*CAUTION- Sublingual Nifedipine should not to be used as it can cause a catastrophic fall in bloodpressure.
References
No references available